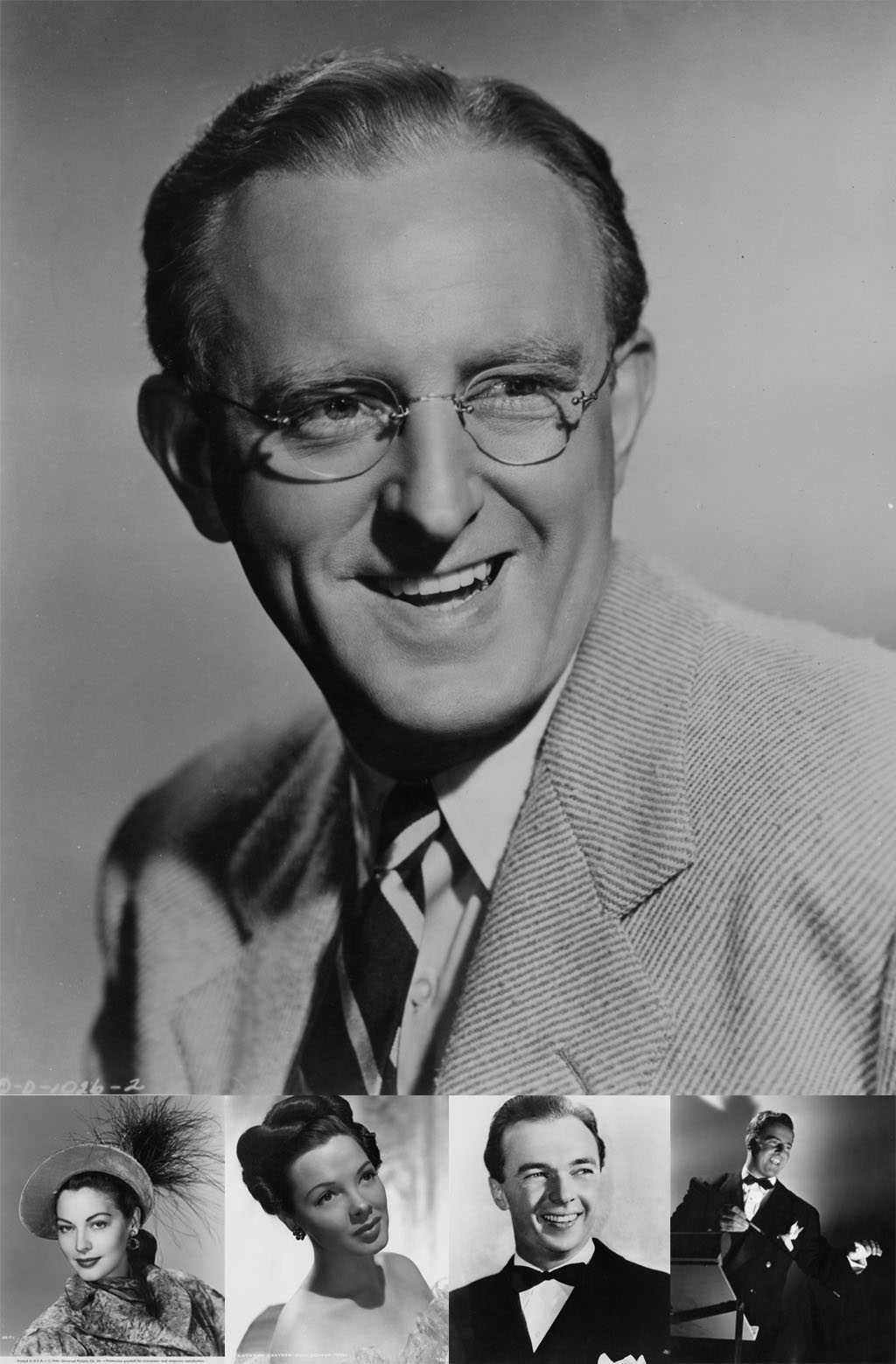
As we left off in our last star-studded post, North Carolina leaders in the post-World War II years sought to improve the medical care and general health in the state through a public awareness campaign known as the Good Health Plan. Launched with the help of a few Hollywood friends, the North Carolina Good Health Association reached out to North Carolinians through print, film, and radio advertising and multiple forms of community engagement.
Advertising
Billboards and car cards were used throughout the state to publicize the name and goals of the plan, such as the needs for improved nutrition and an increase in hospitals.


Community Engagement
To get North Carolina citizens actively involved in campaign, the Good Health Association sponsored contests with prizes for both adults and children. Grade school students competed in oratorical contests (segregated, with one competition for white students and another for black students) in which they were asked to speak about the need for improved health. Prizes for the winners included $500 college scholarships, RCA radios, and state-wide recognition.

To increase awareness of the need for more medical professionals in the state, a Miss North Carolina Student Nurse pageant was established, with Kay Kyser himself on hand to crown the first winner.
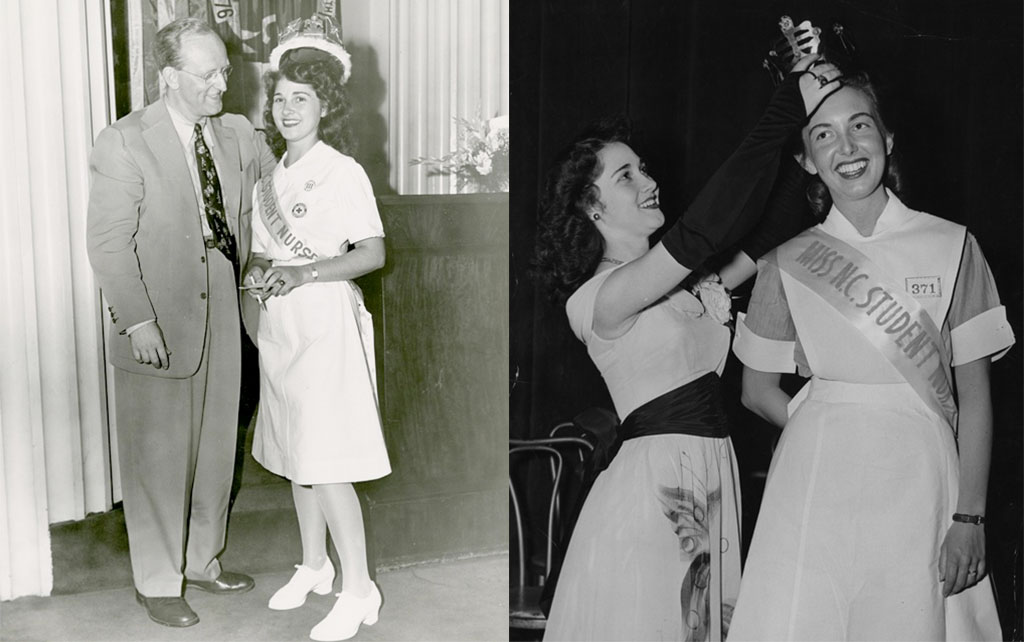
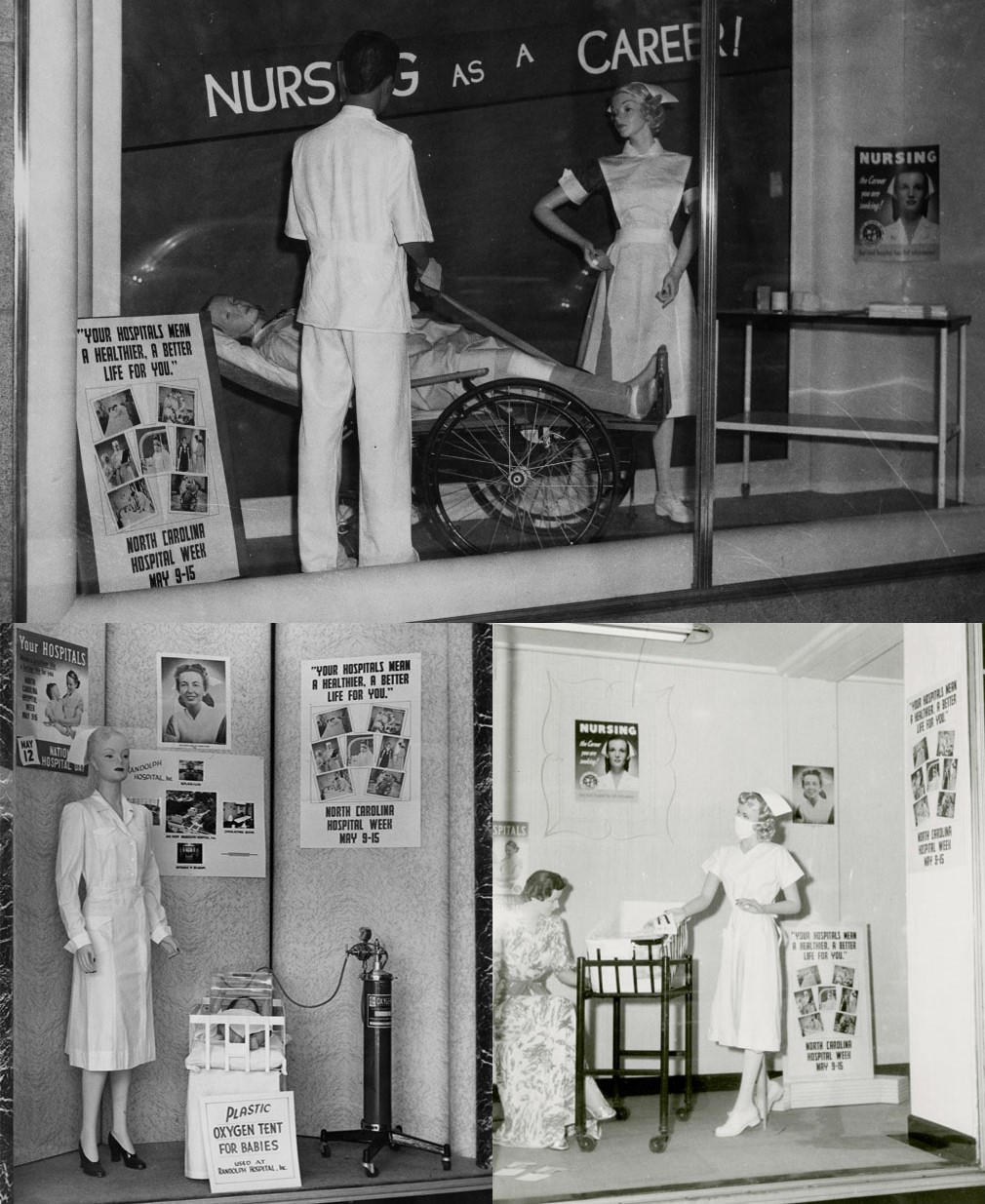
A store window display contest was sponsored to encourage support for the building of local hospitals and to encourage women to pursue nursing as a career.

In conjunction with the national Hospital Survey and Construction Act (which provided federal grants and guaranteed loans to improve the country’s hospital facilities), the Good Health Campaign provided funding to increase medical care in underserved areas, including creating more hospitals (adding over 7,000 hospital beds) and training opportunities for medical professionals. This included the founding of the state’s first four year medical school at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in 1950. In addition, the public relations campaign helped to increase awareness of health and nutrition issues throughout the state in the post-World War II years.